|
The Higgs
mechanism, originally proposed by the British physicist Peter
Higgs (building
on a previous suggestion by Philip
Anderson in condensed
matter physics), is the mechanism that gives mass
to all elementary
particles in particle
physics. It makes the W boson different from the photon,
for example. It can be understood as an elementary case of tachyon
condensationwhere the role of the tachyon is
played by a scalar
field called
the Higgs field. The massive quantum excitation of the Higgs
field is also called the Higgs
boson.
Actually, this mechanism was anticipated by Ernst
Stückelberg in
1957 before Higgs. See theStückelberg
action for
more details.
The breakthrough of Higgs (which was independently
discovered by Brout and Englert at theUniversité
Libre de Bruxelles and
by G. S. Guralnik, C. R. Hagen and T. W. B. Kibble at the
Imperial College) was to give mass to a vector
boson, a.k.a. gauge
boson, by coupling it to ascalar
field. This was done in the context of a spontaneous
symmetry breaking model,
of the type constructed by Yoichiro
Nambu and
others in an attempt to explain the strong
interactions. (These sorts of models were also
inspired by work in condensed matter theory, notably by Lev
Landau and Vitaly
Ginzburg).
For an example of spontaneous symmetry-breaking, imagine a complex scalar
field whose value at each point in space is
-
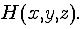
-
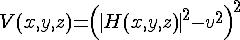
integrated over space. It is non-negative, and there is a
continuous manifold of
minima at
-
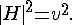
What this means in less technical terms is that the potential
energy density,
as a function of 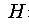 ,
looks like the bottom of a wine bottle: a hump in the middle
and a circular valley around it. (One visualizes the complex
field value as a 2-dimensional plane, the Argand diagram,
and the potential as the height above the plane.) ,
looks like the bottom of a wine bottle: a hump in the middle
and a circular valley around it. (One visualizes the complex
field value as a 2-dimensional plane, the Argand diagram,
and the potential as the height above the plane.)
The point 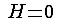 is
symmetric with respect to the U(1) symmetry that
changes the complex phase of is
symmetric with respect to the U(1) symmetry that
changes the complex phase of 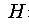
as 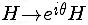 (and
more generally, with respect to SU(2) x U(1) electroweak
symmetry, for example), it is disfavored energetically. The
Higgs field will roll "down the hill" and settle to a stable
value (and
more generally, with respect to SU(2) x U(1) electroweak
symmetry, for example), it is disfavored energetically. The
Higgs field will roll "down the hill" and settle to a stable
value 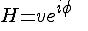 for
some randomly chosen value of for
some randomly chosen value of 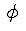 .
This induces an asymmetry of the vacuum, in the sense that
the ground state is not invariant under the U(1) symmetry,
which transforms one value of .
This induces an asymmetry of the vacuum, in the sense that
the ground state is not invariant under the U(1) symmetry,
which transforms one value of 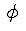 to
a different one. to
a different one.
The problem in using a spontaneous symmetry-breaking model
in particle physics is that, according to a theorem of
Jeffrey Goldstone, it predicts a massless scalar particle,
which is the quantum excitation along the direction of
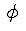 ,
a so-called Nambu-Goldstone boson. There is no potential
energy cost to move around the bottom of the circular
valley, so the energy of such a particle is pure kinetic
energy, which inquantum
field theory implies
that its mass is zero. But no massless scalar particles were
detected. ,
a so-called Nambu-Goldstone boson. There is no potential
energy cost to move around the bottom of the circular
valley, so the energy of such a particle is pure kinetic
energy, which inquantum
field theory implies
that its mass is zero. But no massless scalar particles were
detected.
A similar problem in Yang-Mills theory, a.k.a. nonabelian gauge
theory, was the existence of massless gauge
bosons, which (apart from the photon)
were also not detected. It was Higgs' insight that when you
combined a gauge theory with a spontaneous symmetry-breaking
model, the two problems solved themselves rather elegantly.
Higgs had found a loophole in the Goldstone theorem: when
you couple the scalar to the gauge theory, the massless  mode
of the Higgs combines with the vector boson to form a
massive vector boson. mode
of the Higgs combines with the vector boson to form a
massive vector boson.
Higgs' original article presenting the model was rejected by Physical
Review Letters when
first submitted, apparently because it didn't predict any
new detectable effects. So he added a sentence at the end,
mentioning that it implies the existence of one or more new,
massive scalar bosons, which don't form complete
representations of the symmetry. These are theHiggs
bosons.
Before the symmetry-breaking, all elementary particles
(except the Higgs boson itself) are massless and the
symmetry is unbroken, much like the rotational symmetry of a
pencil that stands on its tip. However, the scalar field
spontaneously slides from the point of maximum energy in a
randomly chosen direction into a minimum - much like the
pencil that eventually falls. Important is that the symmetry
doesn't disappear, it is just hidden. One says that the
original symmetry is broken and elementary particles - such
as the leptons, quarks,
W boson, and Z boson acquire masses. The origin of the
masses can be interpreted as a result of the interactions of
the other particles with the "Higgs ocean".
The Higgs mechanism was incorporated into modern particle
physics by Steven
Weinberg and
is an essential part of the Standard
Model.
A slightly more technical presentation of the Higgs
mechanism, which presumes at least an elementary knowledge
of quantum field theory, is reviewed in the article on the Yukawa
interaction.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Newest
articles
|

